The Future of Travel Payments: How Ready Are Travellers to Embrace Cryptocurrency?
Other Articles

A Comparative Study of Chinese and Korean Consumers' Intentions to Adopt Cryptocurrency Payments in Hospitality and Tourism
Study conducted by Prof. Seongseop (Sam) KIM and his research team

The recent announcement by the Hong Kong government regarding its regulatory framework for stablecoins has sent ripples through the financial and retail sectors, with the tourism and hospitality industries now joining the conversation. As stablecoins—cryptocurrencies pegged to stable assets—gain legitimacy, businesses are increasingly considering the integration of cryptocurrency payments into their operations. This policy shift has reignited debate about the readiness of consumers, particularly travellers, to adopt such innovative payment methods.
Prof. Seongseop (Sam) KIM, Professor of the School of Hotel and Tourism Management at The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, and his research team have sought to explore and compare the behavioural intentions of Korean and Chinese travellers towards adopting cryptocurrency payments, especially in relation to the already dominant mobile payment systems. The study was published in Current Issues in Tourism [1].
The purpose of this study was threefold: first, to examine the technological and psychological factors influencing travellers' intentions to use cryptocurrency and mobile payments; second, to apply and extend the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) by incorporating dimensions such as perceived security, risk and convenience; and third, to analyse cross-national differences between Korean and Chinese consumers. The findings offer timely insights for both academia and industry, as the hospitality and tourism sectors grapple with the implications of digital currency adoption.
The Framework of The Model
To systematically investigate travellers' readiness to adopt cryptocurrency payments, the research team developed a comprehensive research model grounded in TAM. While TAM traditionally focuses on perceived usefulness and perceived ease of use as predictors of technology adoption, the proposed model (Figure 1) extends this framework by integrating additional constructs highly relevant to financial technologies: innovativeness, compatibility, perceived security, perceived risk and perceived convenience. These factors were hypothesised to influence attitudes towards both mobile and cryptocurrency payments which, in turn, would affect the intention to use these payment methods while travelling.
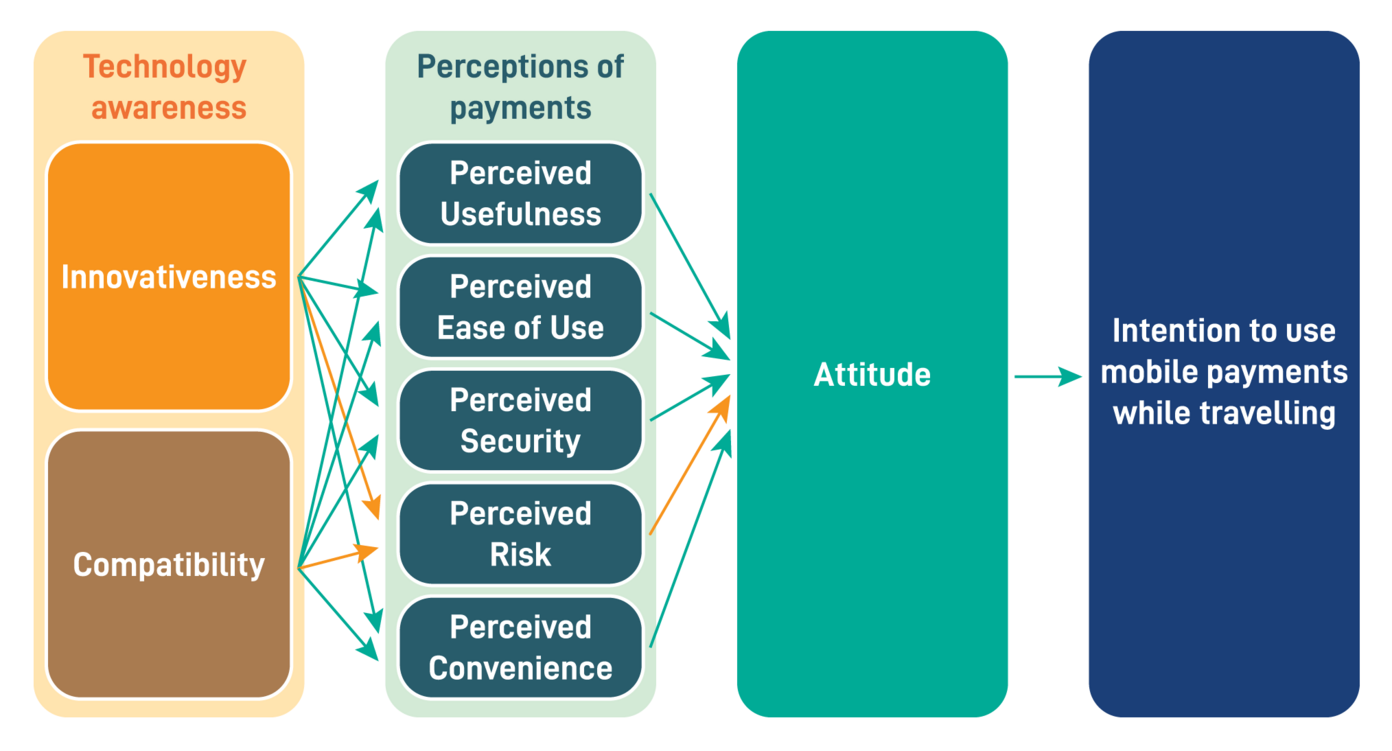
Figure 1. The proposed model: The green arrows indicate the positive impacts and the orange arrows indicate the negative impacts.
Innovativeness refers to an individual’s propensity to embrace new technologies, while compatibility captures the alignment of a payment method with users' values and experiences. Perceived security and risk are particularly salient in the context of digital payments, given concerns about data breaches and financial loss. Perceived convenience, meanwhile, reflects the ease and speed with which transactions can be completed. The model also considered the moderating effect of nationality, recognising that cultural and market differences between China and Korea could shape consumer attitudes and behaviours.
To empirically test the model, the research team conducted a large-scale survey in April 2022. They collected responses from 328 Korean and 355 Chinese participants, all of whom had prior knowledge of cryptocurrencies. The survey instrument, adapted from established scales, measured the nine constructs using a seven-point Likert scale. Structural equation modelling was employed to analyse the data and validate the hypothesised relationships.

Key Findings: Similarities and Differences Across Nationalities
The results of the study reveal both striking similarities and notable differences between Chinese and Korean consumers in their readiness to adopt cryptocurrency payments.
Firstly, innovativeness emerged as a significant driver of positive perceptions towards both mobile and cryptocurrency payments in both countries. Travellers who considered themselves more innovative were more likely to perceive these payment methods as useful, easy to use, secure and convenient. Interestingly, for Chinese respondents, innovativeness did not correlate with perceived risk, suggesting a high level of technological acceptance in China, where mobile payments are already ubiquitous.
Compatibility also played a crucial role, positively influencing perceived usefulness, ease of use and convenience for both payment types and both nationalities. However, among Chinese respondents, compatibility did not significantly affect perceived risk or security, again highlighting the entrenched nature of mobile payments in China and a possible spillover of trust to new payment technologies like cryptocurrency.
When examining the factors shaping attitudes towards mobile payments, clear national differences emerged. For Korean travellers, attitudes were significantly influenced by perceived usefulness, ease of use, security and risk, but not by convenience. In contrast, for Chinese travellers, only perceived security had a significant impact on attitudes towards mobile payments. This divergence likely reflects the maturity of the mobile payment market in China, where convenience and ease of use are taken for granted, and security remains the primary concern.
Turning to cryptocurrency payments, perceived security and risk were the only factors consistently influencing attitudes in both countries. For Koreans, perceived usefulness and convenience also played a role, while for Chinese respondents, these factors were not significant. Notably, perceived ease of use did not significantly affect Koreans' attitudes towards cryptocurrency payments, whereas, for Chinese respondents, it did. These findings suggest that while both groups are open to cryptocurrency payments, the underlying motivations and concerns differ, shaped by their respective payment ecosystems and cultural contexts.
The analysis also confirmed that attitudes towards both mobile and cryptocurrency payments strongly predict the intention to use these methods while travelling. Moreover, the relationship between attitudes and intentions was moderated by nationality, underscoring the importance of local context in understanding technology adoption.
Implications for Hospitality and Tourism Practitioners
The findings of this study carry important implications for hospitality and tourism practitioners seeking to navigate the evolving landscape of digital payments.
First and foremost, businesses should prioritise the security and usability of their payment systems. Both Chinese and Korean travellers value secure and easy-to-use payment methods, and these attributes are critical for fostering customer trust and encouraging adoption. For Chinese customers, the perceived security of payment platforms is paramount, while for Koreans, ease of use and trust are particularly influential in shaping attitudes towards cryptocurrency payments.
Given the widespread acceptance of mobile payments in China, hospitality and tourism operators should ensure that their systems are compatible with leading mobile payment platforms and communicate the security features of their services. For Korean customers, there is a growing openness to cryptocurrency payments, provided these systems are perceived as user-friendly and trustworthy. Businesses considering the integration of cryptocurrency payments should therefore focus on simplifying the user experience and clearly articulating the security measures in place.

The study also highlights the need for tailored marketing and communication strategies. For Chinese travellers, messaging should emphasise the safety and reliability of payment systems, addressing any lingering concerns about data protection and fraud. For Korean travellers, campaigns might focus on the innovative and convenient aspects of cryptocurrency payments, positioning them as a cutting-edge alternative to traditional methods.
Furthermore, as stablecoins and other forms of digital currency gain regulatory backing, hospitality and tourism businesses should stay abreast of policy developments and be prepared to adapt their payment offerings accordingly. The Hong Kong government's stablecoin policy is likely to accelerate the adoption of cryptocurrency payments across the region, making it imperative for industry players to build the necessary infrastructure and expertise.
The intersection of policy innovation, technological advancement, and shifting consumer expectations is reshaping the payments landscape in hospitality and tourism. As cryptocurrencies move from the periphery to the mainstream, understanding the factors that drive travellers' readiness to adopt these payment methods becomes ever more critical. This comparative study of Chinese and Korean consumers reveals that while both groups are open to cryptocurrency payments, their motivations and concerns differ in important ways. By focusing on security, ease of use and local context, hospitality and tourism practitioners can position themselves at the forefront of this digital transformation, delivering payment experiences that meet the needs of tomorrow’s travellers.
Prof. Kim has published over 320 papers in refereed international journals. He is one of the most prolific authors in the tourism and hospitality field. He has been recognised by Stanford University as one of the top 2% most-cited scientists worldwide (career-long) in the field of economics and business in 2025, and one of the top 2% most-cited scientists worldwide (single-year) for six consecutive years, from 2019 to 2024. He is also a recipient of the Lifetime Research Achievement Award from the International Council on Hotel, Restaurant, and Institutional Education in 2024 and the Award for Lifetime Achievement in Tourism Research by the International Conference of Tourism in 2024. In addition, he received the Leadership Award from Asia-Pacific CHRIE (APacCHRIE) in 2023.
| References |
|---|
[1] Quan, W., Kim, S., Hailu, T. B., Ahmad, W., & Han, H. (2024). Exploring travelers' readiness to adopt cryptocurrency payment (vs mobile payment), Current Issues in Tourism, 27:17, 2797-2814, DOI: 10.1080/13683500.2023.2240474
 | Prof. Seongseop (Sam) KIM |



