Synopsis 簡介
- A Multidisciplinary Look at Aging and Cognition
- (06252021 lecture video by William S-Y. Wang, with Chinese subtitles)
- 老齡化與認知:多學科研究的探討(王士元06252021演講視頻,附中文字幕)
- Presented at Intervention & Prevention of Neurodegenerative Disease: Building Resilience (ONLINE)
- 中國大灣區神經退行性疾病的預防和干預
- (See also “Language & Cognition across the Lifespan,” the opening lecture video of RCLCN Summer School, by William S-Y. Wang)
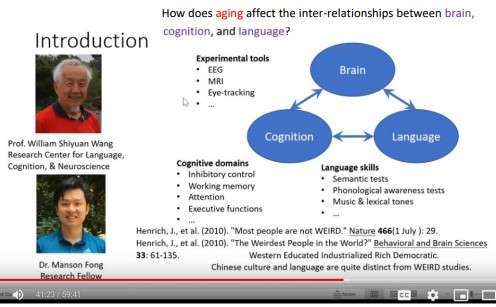
Cognitive Decline and Language (CDL) is part of research at Research Centre for Language, Cognition, and Neuroscience (RCLCN). For the Centre, “The guiding light for our research is to consider the brain, cognition, and language on how the three interact with each other...” as pointed out in the above 2021 lecture video by William S-Y. Wang, “in Hong Kong, in China, we must remember that Chinese culture and Chinese languages are quite distinct from the context in which the WEIRD studies have been made; some may be in common if there are differences we ought to know what these differences are." (WEIRD, an acronym for "Western, educated, industrialized, rich and democratic", cultural identifier of psychology test subjects)
- Note: The screen is from William S-Y. Wang’s lecture in English along with other IPND lectures.
And, "Cognitive Decline and Language: Cumulative References" is a full-text online bibliography and knowledge repository primarily to serve the community at large but also to serve colleagues in Mainland China by keeping updated with international literature. So the bibliography aims to be bilingual if possible with the contents such as the subject indexes and the glossary. The bibliographical contents include phenomena descriptions and explanations about cognitive aging and related neurodegenerative disorders/diseases. Investigation of their causes are explained in neuroscience which consists of multidisciplinary research methods. The roles of language during cognitive aging and neurodegenerative disorders are attentively explored. Control, prevention and interventions to cognitive aging in decline to neurodegenerative disorders are also pointed out in the contents of CDL bibliography.
Full-text. The CDL online bibliography in full-text as a central part of CDL web is arranged as Bibliography A-M and Bibliography N-Z.
Cumulative References. The CDL bibliography in full-text is accompanied/referred by cumulative Abstracts, Indexes (by publication, by author, and by subject) and Glossary; they are compiled and recreated in hope for systematic overview overall of the selected CDL full-text literature. In addition, Database (CDL Reference Database), continuously updated and openly available to the general internet public, could assist to view each individual bibliography entry in details, with some collective-view functions such as by author/creator. As for Visualization, it is a brief visual presentation of CDL bibliographical data. And, Bibliometrics introduces the concept and software of data visualization analysis for finding research patterns and trend of specific topics. Cumulative References in progress can be accessed without password.
-
Acknowledgement. This work is part of a research project at the Research Centre for Language, Cognition, and Neuroscience. Under the direction of William S-Y. Wang and Cho-Yee To (currently at the University of Michigan), it has been indexed and compiled by Yifeng Wu & Andrea Fung with needed help from university librarians, departmental technical colleagues, and CDL research team members.