Research paper titled “Speckle-driven single-shot orbital angular momentum recognition with ultra-low sampling density”, with Professor Puxiang LAI as one of the corresponding authors, was recently published in Nature Communications, an open access, multidisciplinary journal dedicated to publishing high-quality research in all areas of the biological, health, physical, chemical, Earth, social, mathematical, applied, and engineering sciences.
“Speckle-driven single-shot orbital angular momentum recognition with ultra-low sampling density”
[Zhiyuan Wang, Haoran Li], Tianting Zhong, Qi Zhao, Vinu R. V, Huanhao Li, Zhipeng Yu, Jixiong Pu, Ziyang Chen*, Xiaocong Yuan*, and Puxiang Lai*
Nature Communications 16(1): 11097 (2025). doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-66074-3
Abstract
Recognizing orbital angular momentum (OAM) of vortex beams is essential for optical communications and quantum technologies, yet conventional methods struggle in scattering environments and rely on high-resolution sensors. In this study, we propose a speckle-driven OAM recognition technique termed spatially multiplexed points detection (SMPD), which transforms scattering media into efficient encoders. By extracting intensity information from only 16 spatially distributed points in a speckle plane, SMPD achieves over 99% recognition accuracy with a sampling density as low as 0.024%—4096 times lower than conventional imaging-based approaches. The method also demonstrates versatility in spatiotemporally interleaved vortex beam decoding, high-capacity OAM-multiplexed communication, and classification tasks such as MNIST and Fashion-MNIST. This work establishes a scalable, resource-efficient strategy for optical information processing and sensing in complex scattering environments.
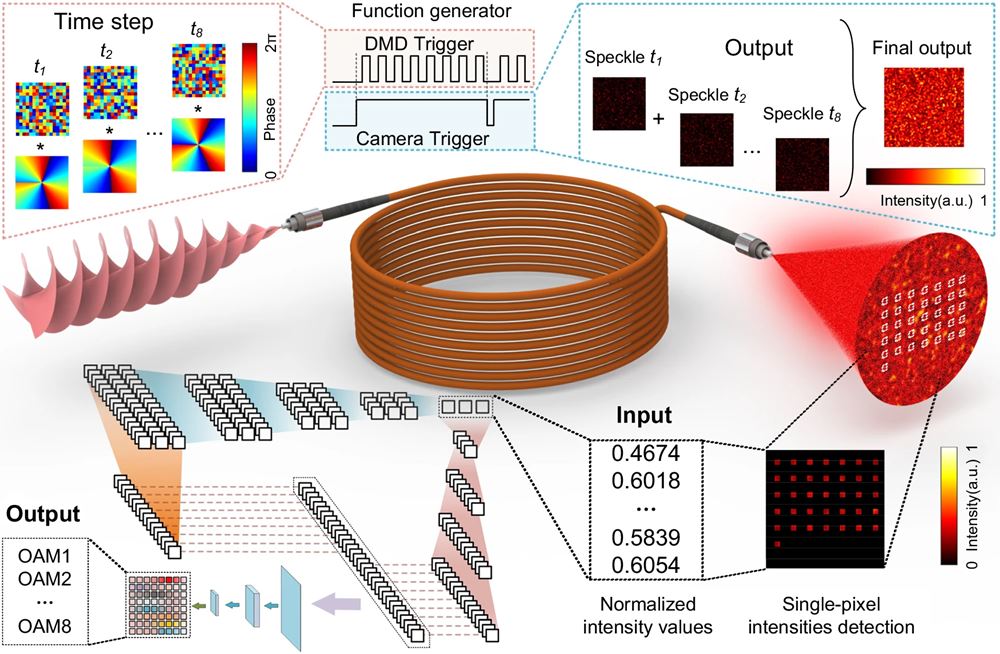
Eight vortex beams with different OAM values are sequentially transmitted through the MMF. The charge couple device (CCD) camera records a single speckle image, representing the spatiotemporally superposition of all beams, synchronized with a digital mirror device (DMD) and a function generator. A sampling mask is applied, and the sampled intensities are input into a modified ROAM-ANN to decode the OAM information.





