- TECHNOLOGIES & SOLUTIONS
- Technologies
- Solutions
INTERNET OF THINGS
IoT has been identified as one of China's strategic emerging industries. In 2012, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology of the People's Republic of China (MIIT) promulgated the Development Programme of the Internet of Things in the Twelfth Five-Year Plan, which undoubtedly bodes very well for China's developing IoT. As the key technology in IoT, RFID is bound to see its application expanded in tandem with the development of the IoT, and being one of the nine key areas for development, smart transport is on track for rapid development and maturing under national planning.
According to the International Telecommunication Union, an IoT refers to a network where the sensor links any object with the Internet according to a protocol, and engages in an exchange of information and communication, in order to achieve intelligent identification, positioning, trace and track, control and monitor, and management1. It is a network extended and expanded based on the Internet.
1國際電信聯盟,「物聯網技術」,物聯網 演義(二)— ITU 互聯網報告 2005:物 聯網 2005 年,2005 年。
The concept of IoT was proposed by the Auto-ID Center of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). At present, the whole world is filled with a variety of interconnected smart devices, and the intelligent era has quietly arrived. In 2009, China's then Prime Minister, Wen Jiabao, put forward the "Reading China" concept in Wuxi, China, which called for the speedy establishment of China's "Reading China” centre and a focus on the development of a new generation of information technology, such as, the combination of IoT and cloud computing. Even since then, a revolution has been in the making under China's IoT era.
IoT and related new technologies are undergoing rapid development worldwide and have been applied to a number of key areas. In 2012, the Chinese market for the IoT industry reached RMB 365 billion, which is an increase of 38.6% compared with 2011. With the rapid development of China's IoT industry and the emergence of industrial scale clusters, an industrial revolution is underway in the era of China's IoT. Specifically, China's IoT technology has been integrated into all walks of life in different areas. Key areas include:
- 1Urban management: Such as, monitoring and intelligent management systems.
- 2Environment and safety tests: Such as, smart waste disposal, automatic monitoring devices, water quality monitoring system, as well as regional ecological monitoring system.
- 3Healthcare: Such as, electronic medical records, medical supplies tracking, quality control systems and wireless comprehensive smart hospitals.
- 4Intelligent transport: Such as, intelligent traffic signal control systems, electronic police system, traffic video surveillance, positioning systems and electronic road pricing. (Figure 1-1)
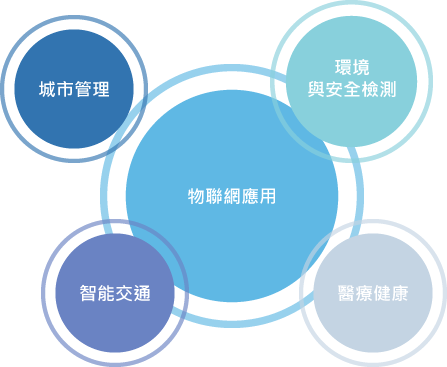 Figure 1-1: Applications of IoT
Figure 1-1: Applications of IoTThroughout the Development Programme of the Internet of Things in the Twelfth Five-Year Plan promulgated by the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology of the People's Republic of China, applications of the IoT in China cover the following areas: smart power grid, smart transport, smart logistics, smart homes, environment and safety tests, industrial and automated control, healthcare, precision farming and national defence.
According to the latest forecast by analyst, Mason, the number of IoT devices will grow to 16 billion by 20202. Independent technology and market research company, Forrester, expects that by 2020, revenue from the IoT industry worldwide will be 30 times the revenue from Internet-related business, and by then, the IoT will have connected more than 100 billion devices. Wang Jianzhou, former Chairman and CEO of China Mobile, China's largest mobile communications service provider, expects in the next decade, 50 billion devices will be connected to the IoT3. IoT Industry Alliance Z-Park expects that China's IoT industry will reach one trillion yuan by 2015; until 2020 and more than 5 trillion yuan by 20204.
A complete IoT system consists of four layers: the sensor layer, the network layer, the platform layer and the application layer (Figure 1-2).
2 英國每日電訊報,2010 年 11 月 3 日。
3 林妍,「物聯網安全嗎?嬰兒監控器夜半驚魂」,大紀元,2014 年 5 月 14 日。
4 台灣區電機電子工業同蘇公會,「下個兆元通訊產業 - 商機超越網際網路 30 倍」。
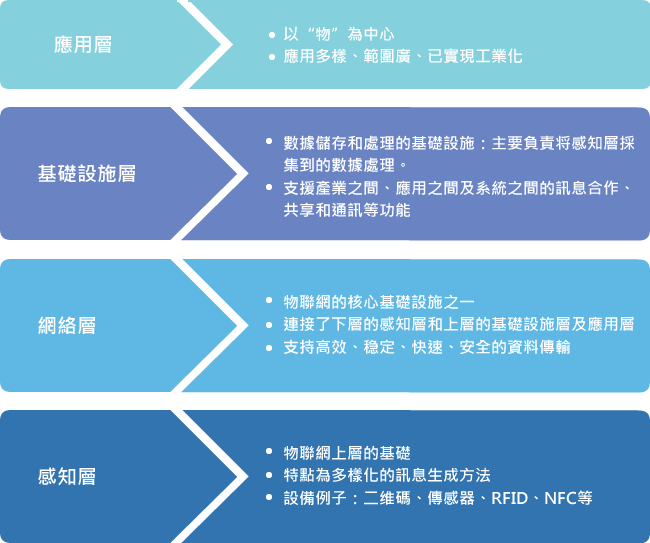 Figure 1-2: Component layers of an IoT system
Figure 1-2: Component layers of an IoT system In view of its potentials in development and application, IoT has been put into rigorous development by various countries in recent years. However, there are several factors that hinder its development, including wide-ranging and changing user needs, a lack of internationally-recognised industry technical standards, nearly exhaustion of the limited IPV4 resources and the security, reliability and privacy doubts and reservations in people collecting large amounts of data, etc. All these bring pressure on and hinder the development of the IoT5.
The following paragraphs introduce the key technologies of the IoT layers.
5 「中國射頻識別(RFID)技術政策白皮書」,RFID 射頻快報,2006 年 6 月 9 日。


