Dr Frank Leung

Dr Leung is an active researcher. He has published over 200 research papers and one book on Computational Intelligence, Intelligent Control, Signal Processing, and Power Electronics. At present, he is involved in the R&D on Intelligent Signal Processing and Robots. He has served as editor, guest editor and reviewer for many international journals. He also helped the organization of many international conferences. Currently, he is Editor of the HKIE Transactions and Guest Editor of Sensors. He is also the Leader of the FENG Robotics Club.

Robot for shooting flying-disc with machine learning

Semi-automatic messenger-robot
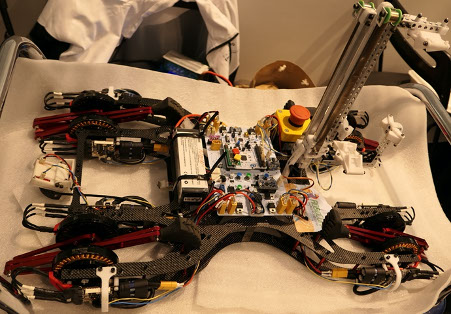
Automatic four-leg robot
Research Highlights:
Dr Leung’s current research focuses on the following three topics:
Intelligent Optimization and its Applications: Hypoglycaemia is a medical term for a body state with a low level of blood glucose. It is a common and serious side effect of insulin therapy in patients with diabetes. The group proposed a system model to measure physiological parameters continuously to provide hypoglycaemia detection for Type 1 diabetes mellitus (TIDM) patients. The contribution include the design of: (1) A model of fuzzy inference system (FIS) for hypoglycaemia detection, and (2) An intelligent optimiser for the FIS parameters.
Structure-Based Drug Design Using Computational Intelligence Techniques: Imbalanced datasets are commonly encountered in real-world classification problems. Re-sampling has become an important step to pre-process imbalanced data. A sampling strategy that is based on both over-sampling and under-sampling is proposed. The contribution is a hybrid pre-processing method (FRB+CHC) to re-sample imbalanced datasets that: (1) Creates the new samples of the smaller class based on fuzzy logic, and (2) Improve the datasets by the evolutionary computational method that under-samples both the minority and the majority samples.
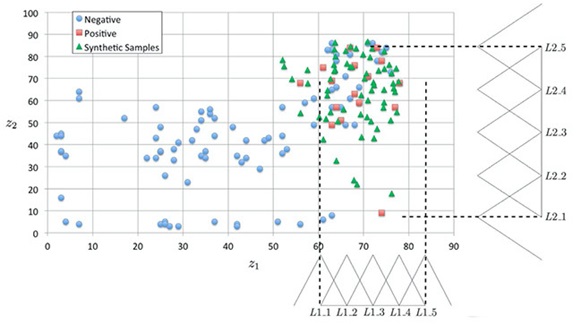
Distribution of the samples after over-sampling. The y-axis represents the values of z2 and x-axis represents the value of z1
Identification of protein-ligand binding site is an important task in structure-based drug design and docking algorithms. Different methods have been developed to predict the binding site. When scores are calculated from these methods, the algorithm for doing classification becomes very important for the prediction. The group propose the use of support vector machine (SVM) to cluster the pockets that are most likely to bind ligands based on selected attributes. The approach offers improved results over other well-known methods on the dataset LigASite and 198 drug-target protein complexes.
A Computational Intelligence Based Classifier and its Applications: Microphone recognition aims at recognizing different microphones based on the recorded speeches. In the literature, Gaussian Supervector (GSV) has been used as the feature vector representing a speech recording, which is obtained by adapting a Universal Background Model (UBM). The team looked into GSV in detail. To improve the quality of the raw GSV, it is proposed that a kernel-based projection method that maps the raw GSV onto another dimensional space. The contribution include: (1) Confirming that GSV can outperform the averaged frame-level features, (2) Finding how GSV is affected by the UBM and other parameters, and (3) Separating the microphone response information and the speech information into different dimensions in the projected feature space for improved microphone recognition.




