Central π-conjugated extension in quinoxaline-based small-molecule acceptors as guest components enabling high-performance ternary organic solar cells
Kwok, Chung Hang ; Ng, Ho Ming ; Gao, Chuanlin ; Hu, Huawei ; Dela Peña, Top Archie ; Lai, Joshua Yuk Lin ; Chen, Li ; Xie, Lan ; Li, Mingjie ; Wu, Jiaying ; Zhang, Guangye ; Wong, Wai-Yeung ; Yan, He ; Yu, Han
Journal of Materials Chemistry A, Materials for Energy and Sustainability • Published on 17 April 2025
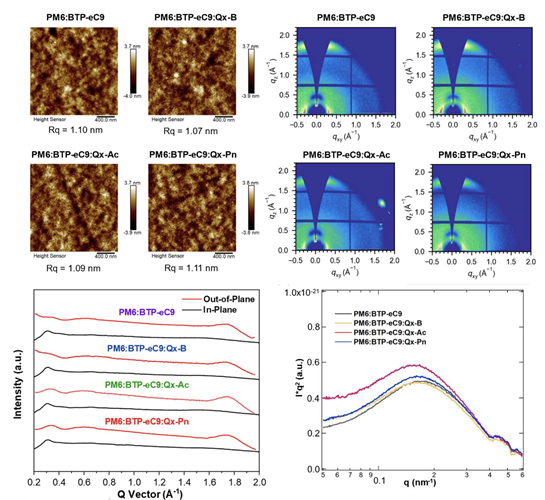
Ternary strategies have critical roles in pursuing high efficiencies for organic solar cells (OSCs). However, the optimization of ternary systems relies heavily on understanding the compatibility and performance of different guest/host combinations. To establish design principles of quinoxaline (Qx)-based small-molecule acceptors (SMAs) as guest components for ternary OSCs, a new Qx-SMA named Qx-Ac and two reported Qx-SMAs named Qx-B and Qx-Pn were synthesized by extending the central Qx core with benzene (B), acenaphthene (Ac) and phenanthrene (Pn), respectively. After blending with PM6:BTP-eC9 (17.55%), Qx-Ac (18.51%) and Qx-Pn (18.11%) devices exhibited superior phase segregation and lower energy disorder. The improvement in Qx-Pn devices was dampened by inferior absorption, while the use of Qx-B (17.56%) did not improve the device at all. This work delineates the significant influence of Qx core extension on ternary guest compatibility, providing valuable insights and guidance for the design of ternary systems towards higher efficiencies for OSCs.