Definition
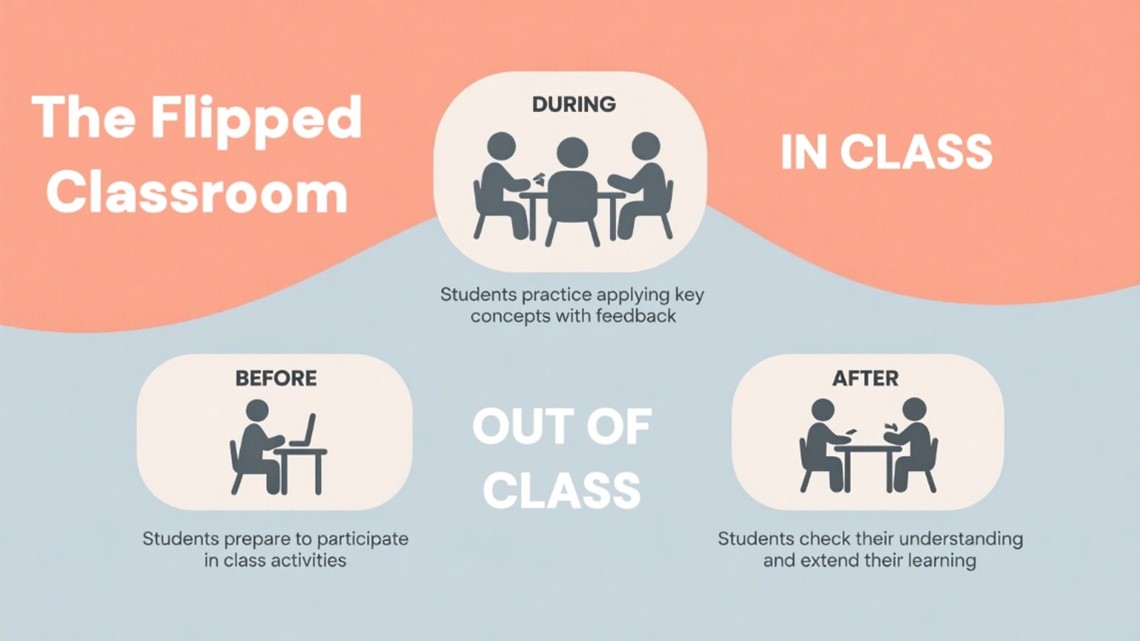
The flipped classroom is an effective teaching approach that inverts the traditional instructional process. Students are expected to learn knowledge independently before class by using learning materials such as videos, readings, or podcasts. Classroom time is dedicated to teacher-student interaction, collaborative inquiry, the application of knowledge and so on, with consolidation taking place after class (Persky & McLaughlin, 2017). This approach emphasises a student-centred model, enabling students to take responsibility for their learning and providing them with opportunities to apply their knowledge in a collaborative and engaging environment (Agirman & Ercoskun, 2022).
Source: The picture was generated by DouBao AI.
Benefits and Challenges
Flipped learning has been shown to offer many benefits, including increased student engagement, improved academic performance, and enhanced critical thinking skills. This approach also enables teachers to devote more class time to application and problem-solving activities, rather than simply delivering lectures, which can result in deeper learning and higher retention rates (Fedotova & Latun, 2016).
While flipped learning offers numerous benefits, there are also potential challenges associated with this approach. For example, it requires students to take responsibility for their learning, which can be challenging for those who struggle with self-motivation or self-regulation. Students may find it difficult to remain focused and engaged when reviewing instructional materials independently, which can negatively affect their learning outcomes (Bishop & Verleger, 2013). Flipped learning also demands that teachers develop new skills and strategies for designing and delivering instructional materials, as well as for facilitating active learning activities during class time (Kunwar, Shrestha & Adhikari, 2025). This can present a significant challenge for teachers who are accustomed to traditional lecture-based methods.
Integration of Advanced Technologies for Effective Implementation of Flipped Classroom
The integration of advanced technologies, including the prevalent use of tablets and smartphones as well as access to generative AI, has the potential to address challenges associated with traditional flipped learning, thereby enhancing the effectiveness and engagement of this instructional approach for students. On the one hand, it is possible to enhance students’ motivation or self-regulation by integrating intelligent Learning Management Systems (LMS), learning analytics and behaviour monitoring technologies, as well as interactive learning materials. By providing personalised learning pathways, progress tracking, and instant feedback, students can be supported in setting learning goals and strengthening their self-regulation abilities. Utilising big data and learning analytics enables real-time monitoring of students’ learning behaviours, identification of learning difficulties, and the timely delivery of reminders or support resources to help students maintain their motivation. Embedding quizzes, interactive Q&A, and gamified elements within learning materials can make learning tasks more interesting and challenging, thereby stimulating students’ intrinsic motivation and improving their engagement and concentration.
On the other hand, teachers in flipped classrooms need to master new skills in instructional design and classroom management, which can be supported through AI-driven instructional design tools, professional development platforms, and classroom interaction and collaboration tools. AI-powered instructional design platforms can assist teachers in quickly creating high-quality videos and interactive courseware, lowering technical barriers. Online training, teaching communities, and virtual seminars support teachers in learning about the flipped classroom approach, technology integration, and classroom management strategies. Real-time polling, collaborative whiteboards, and group discussion platforms can promote active participation and collaborative learning in class, helping teachers to better facilitate student interaction.
In summary, the integration of advanced technologies not only helps students overcome challenges in autonomous learning but also supports teachers in smoothly transitioning to new teaching models, thereby improving the overall effectiveness of flipped classroom implementation.
Reference
Agirman, N., & Ercoskun, M. H. (2022). History of the flipped classroom model and uses of the flipped classroom concept. International Journal of Curriculum and Instructional Studies, 12(1), 78-88.
Bishop, J., & Verleger, M. A. (2013, June). The flipped classroom: A survey of the research. In 2013 ASEE annual conference & exposition (pp. 23-1200).
Fedotova, O., & Latun, V. (2016). Flipped learning as an alternative pedagogical approach to training graduate students: advantages and disadvantages. In EDULEARN16 Proceedings (pp. 2919-2925). IATED.
Kunwar, R., Shrestha, S. K., & Adhikari, S. (2025). The interplay between flipped learning, teacher professional development, and learner autonomy in higher education.
Persky, A. M., & McLaughlin, J. E. (2017). The flipped classroom–from theory to practice in health professional education. American journal of pharmaceutical education, 81(6), 118.
